>>>Notes for Revelation can be found HERE <<<
The three-fold outline of the book Revelation one is found in verse 1:19. Notice that Jesus says, talking to John, “Write the things that you have seen, the things which are, and the things that shall take place after these things.” If you look through the Book of Revelation, you’ll find that the phrase “after these things” is repeated over and over. And why is that? I think John is emphasizing to us that there is an orderly development of how things are going to happen. Some of it’s difficult to understand. Some of it we probably can’t fully grasp. But John wants us to understand that what is coming during the seven years of tribulation is going to be a very orderly, systematic judgment of God on the Earth. So he says, “Write the things that you have seen,” in the past tense. Right? So, what has John seen in the past in Revelation chapter one? The vision of Christ. He’s recorded that for us. “And the things which are” represent chapters two and three which deals with the seven churches of Asia. “The things that will take place after this,” represent Chapters four through 22. So, John really gives us his own outline. And if we just follow that outline, it’ll save us from a lot of confusion.
In the first few chapters, we have the seven churches as John ministered to them. In Chapters four and five, we see the church in heaven. There are certain things that are said that tell us that that can only be the church in heaven, which fits with our understanding of the rapture of the church. What do we read in Revelation 4:1? “I heard a voice saying, ‘Come up here.’”. Then in Chapters six through 19, we have the tribulation period itself. It’s very interesting to notice, the word church occurs 19 times in the first three chapters. It does not occur from Chapters six to 19 — the section that deals with the tribulation period. Instead, who do we read about? The nation of Israel. Remember that Paul tells us in Romans 11:25. “Blindness, in part, has happened to Israel.” God is faithful to His promises; what about the nation of Israel? Is God finished with the nation of Israel? Their time is yet coming, and that’s going to be the tribulation period. So, in chapter six through 19, we read about Israel. We read about the tribes. We read about Jerusalem. The whole focus goes back to the promised land.
So let’s go back to Revelation 1:1. “The revelation of Jesus Christ, which God gave to Him to show His servants things that must shortly take place and He Jesus sent and signify it by His Angel to his servant, John.” So, this book has been passed down from the Father to the Son to an angel to John. “Who bore witness of the Word of God in the testimony of Jesus Christ to all things that He saw. Blessed are those that read and hear the words of this prophecy and keep the things that are written in it for the time is near.” Because the Book of Revelation deals with everything from the time of John till the end of the Kingdom. No matter where you live in that time, the time is near because whatever is next to come is going to come and it’s going to come quickly. We notice several purposes behind the book: 1) to reveal Jesus Christ, 2) to reveal the course history, 3) to finish John’s testimony, and 4) to bless those who study the book and not only study but obey the book.
John identifies himself now in Revelation 1:4, “John to the seven churches which are in Asia.” This a typical opening of a letter in the ancient world; you identified yourself first and then identified who you’re writing to. “Grace to you and peace from Him, who is and who was and who is to come. And from the seven spirits who are before the throne.” So, what is “who is and who was and who is to come?” They mean that He’s infinite, and eternal. “The seven spirits before his throne” harkens to Isaiah 11:2, which lists the spirits of God having seven characteristics. So essentially, he’s talking about the Holy Spirit. The interesting thing to me at this point, in the first four versus we have the Father, we have the Son, we have the Holy Spirit, and they’re all sending greetings to us. They’re all working for our spiritual well-being.
Revelation 1:5 says, “From Jesus Christ, the faithful witness, the first born from the day of the ruler over the kings of the earth. To him who loved us and washed us from our sins in his own blood.” This is talking about the finished work of Christ on the cross, the one who provided for us our so great salvation. Revelation 1:6 should really excite us, “and has made us kings and priests.” In all the Old Testament, you never read of a prophet, priest, and king together. Jesus is prophet, priest, and king. Here, we’re told, “He has made us kings and priest.” You can go to 1st Peter 2:9, where Peter reminds us that we are a royal priesthood. There was no royal priesthood in the Old Testament, with one exception: Melchizedek the King priest.
Revelation 1:7 says, “Behold, He is coming with clouds.” I don’t know about you, but I long for it more and pray for it more every day. “He is coming with clouds and every I will see him. Even they who pierced him, and all the tribes of the earth will mourn because of him.” Which coming is John talking about — the Rapture or Jesus’ second coming? Ask yourself the question, at the rapture will every eye see Him? No, not unbelievers. It’s going to be a secret departure. They will not see him. We will simply be gone. So, we know we’re talking here about the second coming. “All the tribes in the earth will mourn because of him.” Revelation 1:8 says, “I am the alpha and the omega, the beginning and the end says Lord.” Which “beginning” is this? Go back as far as you want. “In the beginning, God created the heavens and the earth.” That’s the beginning of creation. And then we have in John 1:1, “ In the beginning was the word.” What beginning is he talking about? As far back as you want to go into eternity past, and whatever beginning you can imagine and He was there. That’s the one “who was.” In first John 1:1 says, “That which you heard from the beginning.” You might remember too in Mark 1:1, “The beginning of the gospel of Jesus Christ,” a different beginning. Here in Revelation 1:8, the Lord says, “I am the beginning, and the end says the Lord, who is and who was and who is to come. The Almighty.” What amazing statement of His dignity and glory and majesty.
In Revelation 1:9, John begins to describe for his congregations the conditions of his vision. “I, John, your brother and companion in the tribulation and kingdom and patience of Jesus Christ.” We’re all in this together as children of God. He continues, “I was on the island that is called Patmos” off the coast of Turkey, “for the word of God and for the testimony of Jesus Christ.” In other words, under persecution under Emperor Domitian, John was having too much effect, just like Paul was earlier. But unlike Paul, who was executed for his testimony, Domitian just shut him away on the Isle of Pattern of Patmos so John could write Revelation.
Gene Cunningham - September 7, 2022
The Outer Darkness Controversy - Part Three
From Series: "Jesus' Roadmap for the Future"
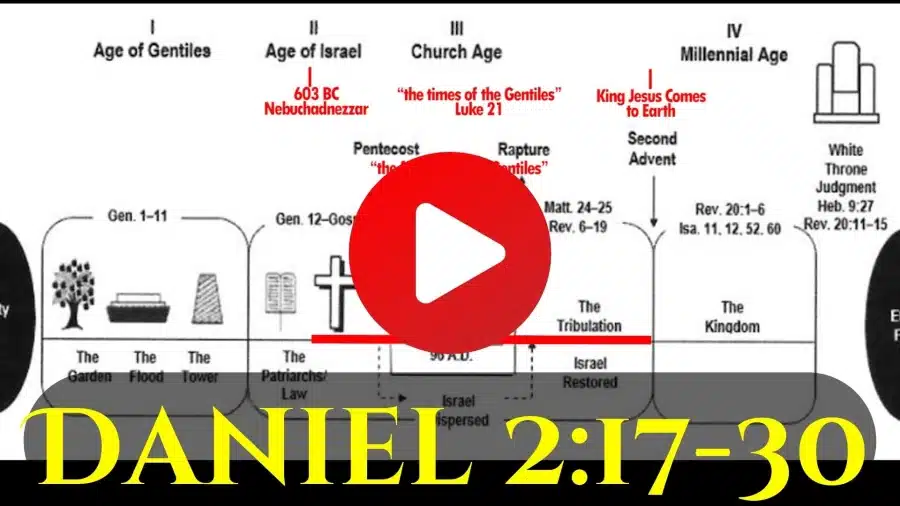
The Olivet Discourse -- Jesus' Roadmap for the future, is one of the three major discourses (sermons) of Jesus. They include: 1. The Sermon on the Mount/Galilee Discourse (Matthew 5–7) 2. The Olivet Discourse (Matthew 24–25; Mark 13; Luke 21 3. The Upper Room Discourse (John 13–17) Each of these messages is aimed at a specific period of history, which we call a dispensation. They lay out God’s dispensational plan, like a road map, from the time of the crucifixion to the end of time. The Sermon on the Mount was directed to the generation in which Jesus lived and was His platform as King—if Israel would receive Him. Obviously, they rejected Him as their King. However, this will be the basis of Jesus’ administration during the 1,000-year Kingdom Age (Millennium). Then, the Olivet Discourse was aimed at the consequences of Israel’s rejection of Jesus as Messiah, and anticipated the destruction of the nation (70 A.D.) and the final Tribulation period. Remember that the Church Age is an intercalation—meaning an insertion, like a parenthesis, into the Age of Israel. This means that with the Rapture of the Church, the Tribulation picks up where 70 A.D. leaves off. This is why the Church Age is called a “mystery” (Rom. 11:25; 16:25; Eph. 3:1–13; Col. 1:26–27), which is a graduate course to “the principalities and powers in the heavenly places” (Eph. 3:10). Finally, the Upper Room Discourse was directed toward the Church Age, which began at Pentecost and would continue to the Rapture (1 Thess. 4:13–18). The uniqueness of this Age is summarized by Paul’s phrase “in Christ,” and all of the elements involved in what we call “positional truth”—our total union with Christ and the indwelling of His Spirit in us, which occurs nowhere else in history. With the removal of the Body of Christ, the Church, Israel would again become the focus of God’s working on this Earth (Romans 9–11; Revelation 6–19).